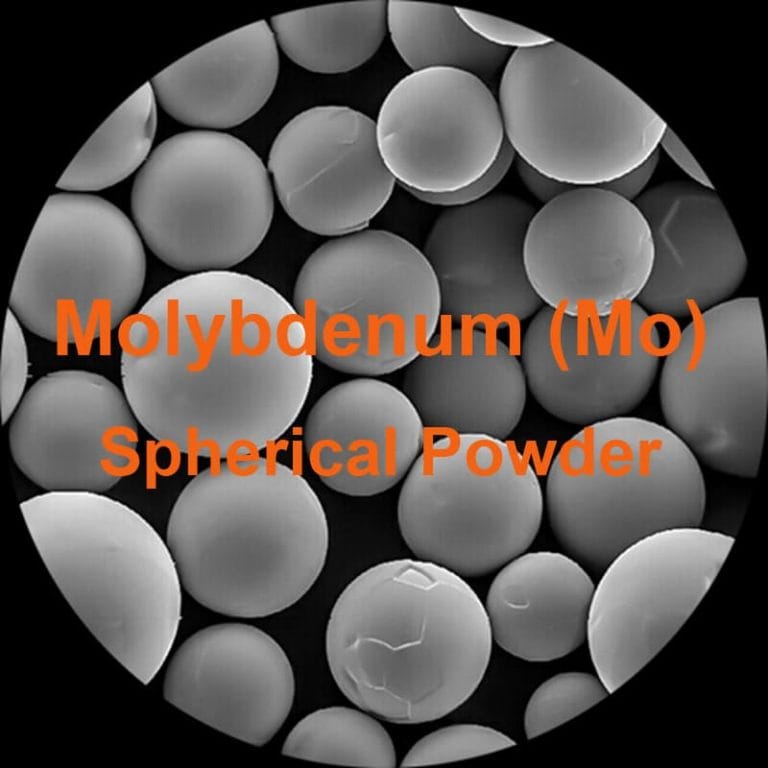
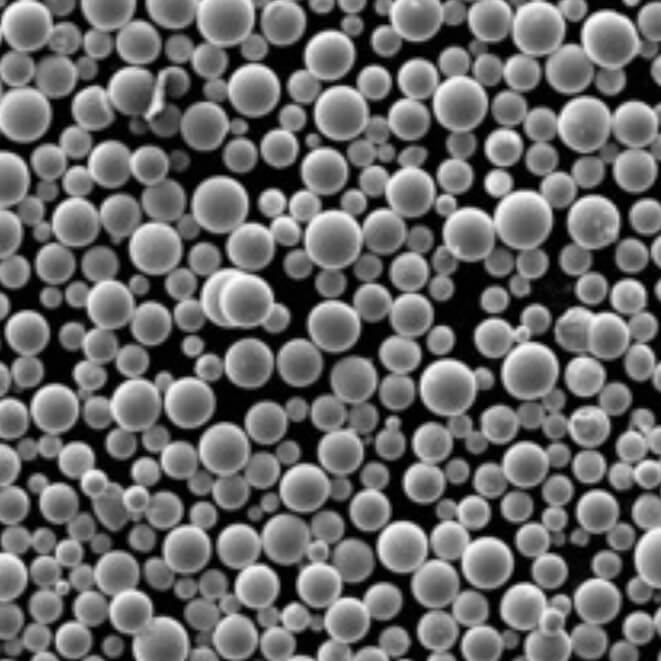
Do You Know About Spherical Powder?
With the advancement of powder applications, the demands for performance have become increasingly stringent. In addition to low impurity content, fine particle size, and precise particle size distribution, certain particle morphology is also required. The particle morphology significantly influences various properties of the powder, such as specific surface area, flowability, fillers, chemical reactivity, and adhesion.
Spherical powders, especially highly dispersed ones, exhibit excellent flowability due to their spherical structure. Additionally, their good dispersibility, larger specific surface area, and unique physical and chemical properties make them highly versatile in a wide range of applications.
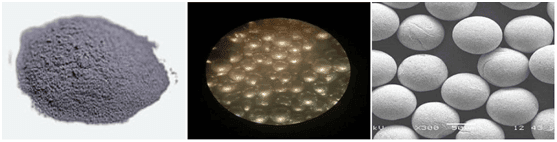
The methods of preparing Spherical Powder:
- Gas flame spheroidization technology (applicable to ceramic materials below 2500°C)
- The irregular-shaped powder particles absorb a significant amount of heat in the presence of a high-temperature gas flame, rapidly melting their surfaces and entering the reactor at a very high velocity. Through the combined effects of rapid air cooling and surface tension, the powder is cooled and solidified into spherical particles before being collected.
- Radiofrequency plasma spheroidization technology (applicable to all metal or non-metal materials)
- The powder particles with irregular shapes absorb a large amount of heat in the high-temperature plasma, the surface melts rapidly and enters the reactor at a very high speed. It is rapidly cooled by gas heat exchange, and under the action of surface tension, it is cooled and solidified into spherical powder.
- Plasma atomization powder-making technology (applicable to all metal materials)
- Due to the conductivity of the ionized gas, the arc energy is quickly transferred and turned into heat energy of the gas, forming a high-temperature gas jet (temperature above 5000°C), which can be used as a high-intensity heat source. Metals and their alloys, ceramics (wires, rods, solid-to-liquid) are melted and atomized through the ultra-high temperature jet generated by the plasma gun through a specially designed feeding device, and finally the spherical micro-nano powder is obtained by controlling the cooling rate body.
- Gas atomization powder-making technology (applicable to metal materials or cermet materials with melting points below 1800°C)
- The molten metal smelted under the condition of vacuum or gas protection heating passes through the heat preservation tundish crucible and the flow-limiting guide tube, and is introduced into the high-pressure gas atomizer. The high-speed gas jet breaks and atomizes the metal liquid into a large number of fine droplets. The liquid droplets solidify into spherical or subspherical powder particles under the action of surface tension during the deposition cooling process.
The Applications of Spherical Powder:
- In the field of thermal spraying: the use of spherical powder results in more uniform and dense coatings due to its excellent flowability. As a result, the coatings exhibit enhanced wear resistance.
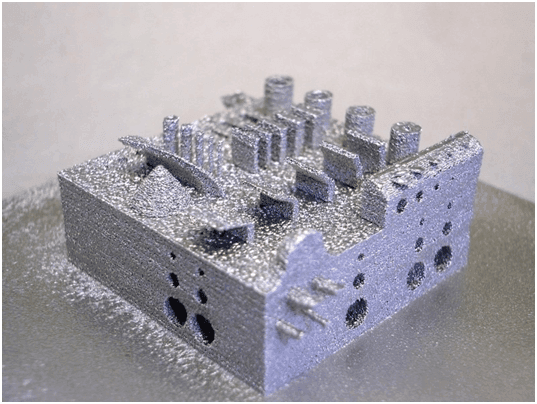
- In powder metallurgy: the use of spherical powder for forming parts leads to high-density components that shrink evenly during the sintering process. This results in products with high precision and excellent performance, providing significant advantages in advanced powder metallurgy forming technologies such as injection molding, gel injection molding, and additive manufacturing (e.g., 3D printing technology).
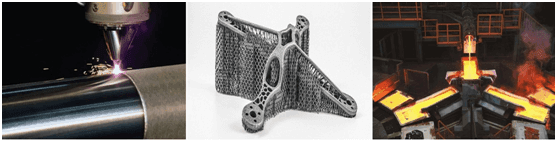
With the continuous advancement of science and technology, the application range of spherical metal powder is also expanding, so the demand for spherical metal powder market is also increasing. The automotive, aerospace, and medical devices segments primarily drive the growth of the spherical metal powder market.
Advanced Powder Tech offers various high-quality spherical powder products at a competitive price. With our expertise and tailored solutions, we can provide the materials you need to meet specific requirements.